Antosovsky, J. et al. The effect of nitrification inhibitor on the yield and quality of Triticum aestivum L. and Brassica napus L. - A long-term experiment. 2025, Field Crops Research, vol 328, DOI 10.1016/j.fcr.2025.109906.
Purpose: The nitrogen is a crucial element in crop production, which can be associated with the environmental loss and low agronomic nitrogen efficiency. The utilization of fertilizers with inhibitors represents an economical option by lowering the number of applications, lowering the dose of nitrogen and limiting the risk of environmental loss of N. Methods: The long-term effect of nitrogen fertilizer with nitrification inhibitors (alternative technology) in comparison with conventional fertilizers (prevalent technology) on yield and quality of winter wheat and oilseed rape cultivated in field conditions at two experimental localities was evaluated. Results: The long-term average yields of both crops were significantly higher after the alternative technology with the NI (+0.4 t/ha wheat grain, +0.3 t/ha rape seed) in comparison with prevalent technology. The effect of NI also resulted in significantly higher average protein content (13 %), protein production (0.98 t/ha) and gluten content (29.5 %) in wheat grain in comparison with prevalent technology without NI (12.8 %; 1.04 t/ha; 28.7 %). The oil content of oilseed rape did not differ significantly between the compared fertilizer technologies. The alternative technology with NI resulted in significantly highest production of oil (+0.1 t/ha) in comparison with prevalent technology. The economic evaluation of alternative technology with NI resulted in net profit in comparison with prevalent technology in every scenario. Conclusions: These long-term results are proving, that addition of NI to the conventional fertilizer applied in higher dose and less applications is more suitable choice compared to the classic split nitrogen fertilization.
Holatko, J. et al. Influence of biochar feedstock blends on soil enzyme activity, nutrient cycling, lettuce biomass accumulation and photosynthesis, 2025. BMC PLANT BIOLOGY, vol.25(1), DOI 10.1186/s12870-025-06352-w.
The thermal conversion of municipal sewage sludge (MSS) offers significant potential for sustainable waste management, particularly through the production of biochar. This study investigates the properties and soil application effects of three biochar types produced via pyrolysis: (i) pure sewage sludge (100%), (ii) sewage sludge blended with sawdust (50%+50%), and (iii) sewage sludge combined with sawdust and zeolite (50%+45%+5%). These biochars were applied at rates of 2.5% and 7.5% (w/w) to arable soil and assessed in an 8-week greenhouse experiment using lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. Brilant) as a model crop. The sewage sludge biochar was characterized by high nitrogen, phosphorus, and water-extractable calcium but exhibited low organic matter and organic carbon content. It enhanced soil enzyme activities related to carbon and nitrogen mineralization without affecting microbial respiration. However, at 7.5% application rate, this biochar caused the highest chlorophyll b content in lettuce, despite acidifying the soil. Adding sawdust to the pyrolysis feedstock significantly increased organic matter, organic carbon (with reduced recalcitrance), and the C: N ratio of biochar. This biochar formulation promoted microbial activity (as indicated by changes in soil respiration) and nutrient cycling, particularly through increased glucosidase activity. Conversely, addition of zeolite to the pyrolysis feedstock reduced the organic matter and organic carbon content while increasing biochar recalcitrance and nutrient immobilization, particularly of sulfur, ammonium, phosphorus, and calcium. At the 7.5% dose, the sawdust + zeolite-enriched biochar improved soil pH and potentially enhanced nutrient retention. However, it did not stimulate microbial enzyme activity or respiration, leading to lower photosynthetic pigment levels and reduced biomassin lettuce, especially at higher application rate. For short-term soil applications under the conditions of this pot trial, the sewage sludge-sawdust biochar demonstrated the most beneficial effects, rapidly stimulating microbial activity and nutrient transformation. In contrast, the sewage sludge-sawdust-zeolite biochar limited nutrient availability and plant growth, suggesting it may be less suitable for immediate soil and plant nutrition. Long-term studies are needed to fully assess the implications of these biochar types for sustainable agriculture. This study highlights the importance of feedstock composition and selection in tailoring biochar properties to meet specific soil and crop requirements.
Klik, B. a kol. Soil environmental monitoring of repurposed railway line operated for 75 years: Case study in Northeast Poland. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2025 vol. 321, Article Number: 100919 DOI: 10.1016/j.dwt.2024.100919.
This study examines the environmental implications of repurposing former railway infrastructure into bicycle paths in northeastern Poland. While lauding the commendable initiative for offering eco-friendly transportation alternatives, the investigation emphasises the potential environmental and consequences linked to contaminated soils resulting from the former railway line, posing risks for both users and the environment. Topsoil samples (0-25 cm) were collected from eight measurement points along the Szczytno- Biskupiec Reszelski railway line (Poland), at varying distances from the railway tracks (5-30 m). Concentrations of specific Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs), notably Ni, Zn, Pb, and Cd, were analysed in 48 topsoil samples. Furthermore, the soil contamination was assessed by contamination indices, single (Igeo, PI) and integrated (RI, (IPln, MERMQ). The study revealed variations in PTE concentrations, with the highest levels recorded at the fourth and seventh sampling sites (4:34.2-57.5 mg/kg; 7:18.2-42.3 mg/kg). These findings were consistently supported by the MERMQ and RI indices, emphasising the significant risks for the environment and increased soil toxicity. In light of the EU's proposed Soil Monitoring Law, the research emphasises the need for robust data collection, analysis, and contamination monitoring practices to facilitate informed decision-making and sustainable environmental management in repurposed transportation infrastructure.
Vlček, V. a kol. Soil organic matter interactions along the elevation gradient of the James Ross Island (Antarctica). SOIL, 2024, Vol. 10, Issue 2, Page 813-826, DOI 10.5194/soil-10-813-2024.
Around half of the Earth's soil organic carbon (SOC) is presently stored in the Northern Hemisphere permafrost region. In polar permafrost regions, low temperatures particularly inhibit both the production and biodegradation of organic matter. Under such conditions, abiotic factors such as mesoclimate, pedogenic substrate or altitude are thought to be more important for soil development than biological factors. In Antarctica, biological factors are generally underestimated in soil development due to the rare occurrence of higher plants and the short time since deglaciation. In this study, we aim to assess the relationship between SOC and other soil properties related to the pedogenic factors or properties. Nine plots were investigated along the altitudinal gradient from 10 to 320 m in the deglaciated area of James Ross Island (Ulu Peninsula) using a parallel tea-bag decomposition experiment. SOC contents showed a positive correlation with the content of easily extractable glomalin-related soil protein (EE-GRSP; Spearman r=0.733, P=0.031) and the soil buffering capacity (expressed as Delta pH; Spearman r=0.817, P=0.011). The soil-available P was negatively correlated with altitude (Spearman r=-0.711, P=0.032), and the exchangeable Mg was negatively correlated with the rock fragment content (Spearman r=-0.683, P=0.050). No correlation was found between the available mineral nutrients (P, K, Ca and Mg) and SOC or GRSP. This may be a consequence of the inhibition of biologically mediated nutrient cycling in the soil. Therefore, the main factor influencing nutrient availability in these soils does not seem to the biotic environment; rather, the main impact appears to stem from the abiotic environment influencing the mesoclimate (altitude) or the level of weathering (rock content). Incubation in tea bags for 45 d resulted in the consumption and translocation of more labile polyphenolic and water-extractable organic matter, along with changes in the C content (increase of up to +0.53 % or decrease of up to -1.31 % C) and a decrease in the C:N ratio (from 12.5 to 7.1-10.2), probably due to microbial respiration and an increase in the abundance of nitrogen-binding microorganisms. Our findings suggest that one of the main variables influencing the SOC/GRSP content is not the altitude or coarse-fraction content (for which a correlation with SOC/GRSP was not found); rather, we suspect effects from other factors that are difficult to quantify, such as the availability of liquid water.
Kučerík, J. a kol. Utilization of Diversified Cover Crops as Green Manure-Enhanced Soil Organic Carbon, Nutrient Transformation, Microbial Activity, and Maize Growth. Agronomy-Basel, 2024, Vol. 14, Issue 9, DOI 10.3390/agronomy14092001.
Studying green manure in several returning methods to enhance soil fertility and crop benefits is a strong foundation for cropland nutrient management. However, how different types of green manures and their variable doses affect the efficacy of applied manures, either buried or mulched, remain overlooked. The objective of this study was to optimize green manure management to enhance soil fertility and maize biomass using five types of green manures (white mustard, forest rye, fiddleneck, sufflower, and pea) in two different doses (low, 5 g per pot, and high, 10 g per pot), which were either buried or mulched before and after maize sowing. Results revealed that total carbon content increased due to green manure treatments, representing a 10% increase over control, particularly through buried w. mustard (10% increase before maize cultivation) and mulched safflower and pea (12% and 11% increase after maize cultivation over control). Dry maize aboveground biomass yields also improved across all variants, with buried mustard yielding 18.4 gplant-1 (compared to 8.6 gplant-1 in the control), mulched mustard yielding 16.4 gplant-1, and buried pea yielding 17.8 gplant-1. Green mulching generally acidified the soil (pH 5.71 compared to 6.21 in the control), except for buried fiddleneck (pH 6.39 after maize cultivation) at a high dose of manures. Carbon-mineralizing enzyme activities (dehydrogenase and beta-glucosidase) were significantly increased by green manures, with buried fiddleneck showing a 22.6% and 20.6% increase over the control, and mulched fiddleneck showing a 24.5% and 22.4% increase under high doses. The study suggests that partially decomposed and mineralized mulched biomass may induce a negative priming effect on carbon-mineralizing enzymes due to a decrease in the C/N ratio of the soil. It emphasizes that the nutrient content and stoichiometry of green manures, alongside soil characteristics such as the C/N ratio, are critical factors for sustainable soil management and carbon sequestration. These findings underscore the need for careful selection and management of green manures to optimize soil health and carbon-storage outcomes.
Kintl, A., a kol. Data on the effect of co-fermentation of maize and leguminous crops on biogas production, methane production and methane content in biogas. Data in Brief, 2024 Vol. 56, DOI 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110842.
The presented set of data brings results of the experimental production of biogas and methane from silages of alternative substrates consisting of maize and three leguminous species with a potential to make the production of biogas more friendly to the environment because the cultivation of legumes is generally considered to be more environment friendly than the cultivation of maize: white sweet clover ( Melilotus albus Medik.), fodder vetch ( Vicia villosa Roth.) and white lupin ( Lupinus albus L.). Obtained data allow to compare the composition of experimental substrates and their important parameters (VS, DM, NDF, ADF, CF, starch, cellulose, hemicellulose, CP, lipids and ADL) as well as the yield of biogas, methane and methane in biogas from silage produced as a monosubstrate from the biomass of maize shreddings on the one side with silages produced from the mixture of biomass from maize and diverse legumes on the other side. This set of data can contribute to awareness about possibilities for reducing environmental risks connected with the cultivation of maize in growers of energy crops and operators of biogas plants. The reason is that a considerable number of farmers do not use new technologies of growing biomass for the production of biogas as they cannot quantify the potential impact on biogas yield and hence on the profitability of biogas plant operation. The measured values demonstrate that silages made from the mixed culture were reaching at least the same production of biogas and its quality as the monocultural maize silage. (c) 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc.
Kalousek P. a kol. The effect of chelating agents on the Zn-phytoextraction potential of hemp and soil microbial activity. Chemical and Biological technologies in agriculture Vol 11(1). 2024 DOI10.1186/s40538-024-00544-6.
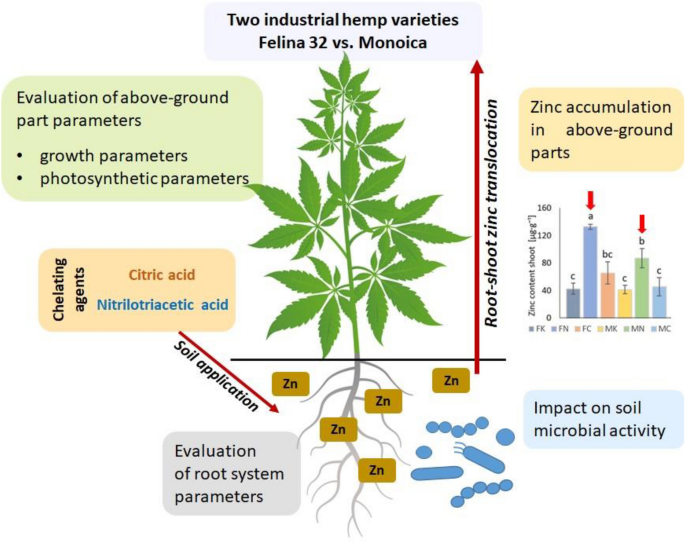
Background Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is a crop with a wide range of uses, from the production of fiber and seeds to the secondary metabolites for medicinal purposes. In addition, it is characterized by high biomass yield and the ability to accumulate heavy metals, which makes this plant convenient for phytoremediation purposes. In this study, the effect of applying exogenous biodegradable chelating agents, citric acid (CA) and nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA), to zinc-contaminated soil on zinc (Zn) uptake by two industrial hemp varieties 'Felina 32' and 'Monoica' was studied. The effect of CA and NTA on available Zn in soils was investigated using an 'in pot' experiment under controlled conditions. The effect of both tested compounds on soil microbial activity was simultaneously evaluated. Results After the application of NTA at a concentration of 5 mmol L-1, a > threefold increased accumulation of Zn in the above-ground parts was recorded in the 'Felina 32' variety. In the 'Monoica' variety, the levels of Zn in the above-ground parts were increased > twofold. NTA affected the soil microbiome negatively, causing decreased enzyme activity (in 'Monoica' planted soil) and induced respiration (in 'Monoica' and especially in 'Felina 32' planted soil). On the other hand, CA application did not lead to significantly increased Zn levels in any of the studied hemp varieties. Together with CA's negative effects on some soil enzymes, CA enhanced urease activity, dehydrogenase and several respiration types for the 'Felina 32' variety and exerted less detrimental effect on the soil microbiome. No toxic effects from increased Zn uptake and accumulation in experimental plants were detected, accounting for the unchanged physiological stress markers (levels of photosynthetic pigments and proline in leaves, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters) and selected growth traits of the above-ground organs and root system. Conclusions From the studied varieties, 'Felina 32' seems to be more suitable for Zn-phytoextraction because of its higher tolerance to increased Zn levels, higher biomass production and Zn accumulation capacity. Our results indicate the potential of using the 'Felina 32' variety in NTA-assisted Zn phytoextraction from contaminated soils.
Kintl A. a kol. Mixed cropping system of maize and bean as a local source of N-substances for the nutrition of farm animals. European journal of agronomy. vol 154, 2024. DOI 10.1016/j.eja.2023.127059. In this study, we investigated the quality of mixed cropping system (MCS) composed of maize and bean in comparison with maize grown as monoculture. Experimental stands were established using the precision vacuum seeding machine during a single crossing of the plot. Inter-row distance was 0.375 m, and regularly alternating experimental crops were maize (Zea mays L.) and common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Experimental variants included maize alone (M) in an amount of 80,000 seeds per hectare and maize (M-MCS) with bean (B-MCS) in a 1:1 ratio (80,000: 80,000 individuals) in MCS. Average yield of N-substances (t/ha) in the biomass obtained from individual variants was 2.36 t/ha in the pure maize culture and 3.09 t/ha in the mixed culture (by 30.9% more). The difference was statistically significant. On the other hand, differences in the content of N-substances (protein) were not found. Results of the experiment for the whole period from 2020-2022 also indicated that the presence of bean in the mixed crop statistically significantly increased contents of acid detergent fibre and crude fibre. On the other hand, compared with the biomass of maize monoculture, bean reduced contents of starch and lipids in the maize biomass. The measured results indicate that biomass from mixed cropping systems has a higher potential to fix more N than biomass from the maize monoculture which is important for digestibility of fodder in livestock production.
